来自:电动星球News

马斯克与牛顿
美国时间 10 月 7 日,特斯拉发表官方博客「Model 3 achieves the lowest probability of injury of any vehicle ever tested by NHTSA」,宣布 Model 3 成为美国国家公路安全管理局有史以来测试过的最安全的车辆(车祸时致伤几率最低的车型), Model S 与 Model X 则紧随其后。
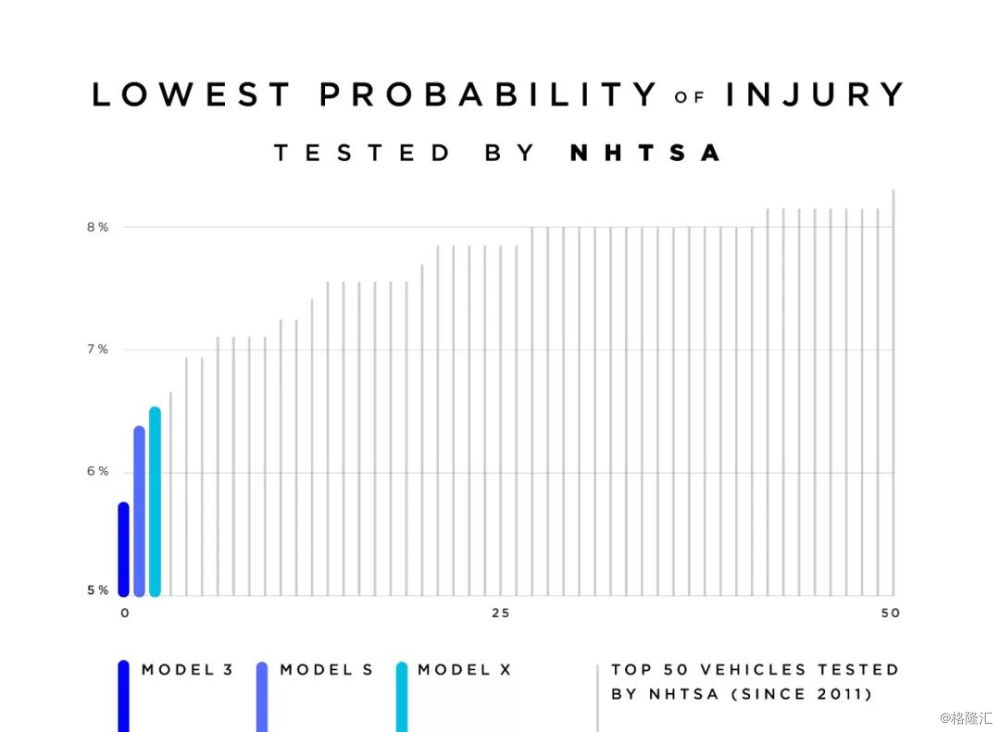
图为自2011年以来NHTSA测试过的 Top 50
早在 17 天前,也就是 9 月 20 日,马斯克就在推特上说,特斯拉会在 NHTSA 正式公布测试数据后发布「汽车安全物理学」文章,「Yes, when it comes to physics, make sure Newton is on your side。」(是的,当涉及到物理时,必须确保牛顿在自己这一边。)

今天这篇官方博客文章,特斯拉果然从物理学角度,完整阐述了Model 3、S/X 的安全策略与设计。
「极惯性扭」这一物理学概念,成为了文章的一大核心主题。结合马斯克早前的发言,破除了前后配重比50:50 就是好设计的误读。
发布了对比奥迪 A4、雷克萨斯 ES 350 的视频,完整解读了其在正面碰撞、小角度碰撞(pole crashes)、侧面碰撞等方面的设计及理念。
当下,电动汽车正面临来自各方面的挑战与质疑,从续航、操控直至隐私与安全。
特斯拉的此次发布,不仅证明电动汽车可以做得很安全,更从物理原理、也就是马斯克念念在兹的第一性原理出发,推导出电动汽车原本就能在结构上做得比燃油车更安全、更易于操纵、有更好的驾乘体验。
不相信?看一下我们翻译的全文,以及根据马斯克推特而做的补充解读。
完整英文附录在后。
enjoy!
————————
特斯拉:在NHTSA测试过的所有车型中,Model 3 致伤几率最低
在已经被NHTSA(美国高速公路安全管理局)认证为车祸致伤几率最小/第二小的 Model S和 ModelX 车身架构基础之上,我们继续将 Model 3 设计成有史以来最安全的汽车。如今,Model 3 不仅在 NHTSA 安全测试中的每一个大项和小项都取得了 5 颗星的成绩,还成为了 NHTSA 安全测试史上致伤几率最小的车型。
Model 3 后驱长续航版的碰撞测试是 NHTSA 新车碰撞测试(NCAP)中的一环,测试内包括了大量的正面、侧面,以及翻滚碰撞测试,并从中计算出车祸造成伤亡的概率。

根据 NHTSA 的数据,Model 3 的乘客在碰撞中受伤的概率,要明显低于市面上其他车型。此前 NHTSA 对 Model S/X 的碰撞测试结果,则仅次于Model 3,排在了第二跟第三位。这也使得特斯拉成为 NHTSA 历史上测试过最安全的汽车品牌。我们相信 Model 3 的其他版本,包括双电机性能版,在未来接受碰撞测试时也会表现出同样优秀的结果。
是什么让 Model 3 更安全?
除了接近 50:50 的前后配重比,Model 3 还拥有极低的极惯性矩,这意味着车内重量最大的零件就位于车辆重心的附近。所以即使 Model 3 没有所谓的“引擎”,却依然拥有中置引擎汽车类似的动态表现,因为它有“中置电池组”,而 Model 3 后驱版的电机正好位于后轮轴之上。这样的车身设计不仅保证了车辆的灵活性和操控感,还将转向动能最小化,从而增强了车身的稳定性。
附加解读:
9月20日,马斯克就曾完整解读过「极惯性扭」这一概念。在马斯克看来,要做好汽车的安全设计,关键在于用好物理原理,「确保牛顿在自己这一边」。而 Model 3 安全设计的关键结束点就在于其极惯性扭做的比其他任何量产车都要好。这对车辆安全、操控性和驾乘感受起到了非常重要的作用,因而是汽车一个非常重要的指标。
马斯克说,不能只看到前后配重比 50:50 这个指标,因为,就算 50:50了,如果质量很大的汽车部件依然远离重心,车辆的操控性依然会不好。从这个角度出发,哑铃的质量分布是不好的,而旋转陀螺的质量分布是好的。
「就好似一个滑冰运动员。相同的重量,但伸出双手后旋转/转动的速度会更快,汽车同样如此。」
马斯克还提供了对「极惯性扭」的术语解释:在汽车世界中,这个术语指的是任何汽车的转向阻力。要弄清楚单个汽车的极矩,您需要分别知道汽车所有部件的重量,以及每个部件与汽车重心的距离。然后将每个部件的重量乘以其距汽车重心的距离的平方。因此,当重量较重的汽车部件远离汽车重心时,会出现较大的极性惯性矩。更简单的解释:保持较重的汽车部件靠近汽车重心,以降低汽车的极矩问题。
正面碰撞
跟Model S/X一样,Model 3也从纯电的动力架构中得益良多,包括刚性极高的乘客舱,经过强化的电池组,还有极低的车身重心。这些基础项目能够有效避免外界因素对车身以及电池组的干扰,降低翻车的风险,以及有系统地把冲击力从车舱内分散出去——还为车前缓冲区吸能效果的进一步优化提供了基础。
安全气囊与约束装置
在碰撞设计、安全气囊、电池安全等方面,我们应用了目前最顶尖的技术与功能:
当正面碰撞发生时,Model 3的缓冲区能够有效控制乘客舱的减速,其先进的乘员约束系统与安全带预张紧器、限力器会协同保证车内乘客的安全。经过特殊设计的安全气囊可以在倾斜或偏置碰撞中有效保护乘客的头部,主动通风孔则会自动调整气囊内的气压以充分优化保护效果。以上所有功能,都是Model 3 5 星安全表现的体现。
小角度碰撞
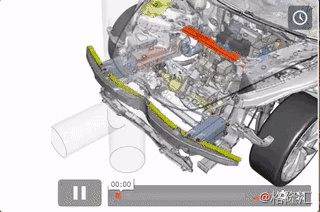
发生在防撞梁的小角度偏置碰撞,也就是造成狭窄碰撞区域的碰撞里面,侧向的吸能区以及斜梁结构能有效减轻碰撞的影响。
这个结构包括了高强度的铝制缓冲梁,以及布置在车辆下前方的活动连接杆。此外还有额外的斜梁,在整个结构没有被碰撞直接影响到的情况下,将冲击力转移到防撞梁上。前悬挂顶部连接着强度极高的马氏体不锈钢梁,在严重的碰撞中能够进一步吸收冲击力。整个结构表面的后部被设计成“U”形。在碰撞中能够弯曲。即使在双电机全驱车型上,这套结构依然能高效工作。
侧面撞击
Model 3 还保持着 NHTSA 测试车型里侧面撞击影响最低的记录。与正面碰撞不同,侧面碰撞留给缓冲区的操作空间并不大,所以我们在尽可能窄的空间里面放入了我们设计的柱状结构和侧梁,以尽可能吸收更多的冲击力。这些部件与高刚性车身、强化电池外壳一起保护车辆免收侧面碰撞的影响。由于车身设计对车内空间干扰不大,我们的侧气囊体积可以做得更大,从而更好地保护车内乘客。
翻滚事故
在美国道路上,翻车事故是人员伤亡的主要来源。特斯拉车型的设计基础是通过尽可能下置的电池组以及融入前后轴的电机,营造极低的车身重心,从而大大减小翻车的可能性。当发生可能引起翻车的碰撞时,我们的内部测试表明,Model 3的车顶能够承受车身四倍的重压,而NHTSA的标准只要求到3倍。
许多车企都希望自己生产的车型在碰撞测试中取得优秀的表现,每一家车企都宣称自己的产品是安全的。但当事故真实发生时,这些测试都表明,如果你开的是一辆特斯拉,那你受伤的几率是最小的。
————————
完整英文:
Model 3 achieves the lowest probability of injury of any vehicle ever tested by NHTSA
The Tesla Team October 7, 2018
Based on the advanced architecture of Model S and Model X, which were previously found by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) to have the lowest and second lowest probabilities of injury of all cars ever tested, we engineered Model 3 to be the safest car ever built. Now, not only has Model 3 achieved a perfect 5-star safety rating in every category and sub-category, but NHTSA’s tests also show that it has the lowest probability of injury of all cars the safety agency has ever tested.
NHTSA tested Model 3 Long Range Rear-Wheel Drive as part of its New Car Assessment Program, a series of crash tests used to calculate the likelihood of serious bodily injury for front, side and rollover crashes. The agency’s data shows that vehicle occupants are less likely to get seriously hurt in these types of crashes when in a Model 3 than in any other car. NHTSA’s previous tests of Model S and Model X still hold the record for the second and third lowest probabilities of injury, making Tesla vehicles the best ever rated by NHTSA. We expect similar results for other Model 3 variants, including our dual-motor vehicles, when they are rated.
What makes Model 3 safe?
In addition to its near 50/50 weight distribution, Model 3 was also designed with an extremely low polar moment of inertia, which means that its heaviest components are located closer to the car’s center of gravity. Even though Model 3 has no engine, its performance is similar to what’s described as a “mid-engine car” due to its centered battery pack (the heaviest component of the car) and the fact that Model 3’s rear motor is placed slightly in front of the rear axle rather than behind it. Not only does this architecture add to the overall agility and handling of the car, it also improves the capability of stability control by minimizing rotational kinetic energy.
Like Model S and Model X, Model 3 benefits from its all-electric architecture and powertrain design, which consists of a strong, rigid passenger compartment, fortified battery pack, and overall low center of gravity. These safety fundamentals help to prevent intrusion into the cabin and battery modules, reduce rollover risk, and distribute crash forces systematically away from the cabin – all while providing the foundation for our superior front crumple zone that is optimized to absorb energy and crush more efficiently. Here, you can see how the orange internal combustion engine block is thrust towards the cabin during a frontal impact test:
We also added state of the art features and new innovations in crash structure design, restraints and airbags, and battery safety to the core of Model 3’s design:
In frontal crashes, Model 3’s efficient front crumple zone carefully controls the deceleration of occupants, while its advanced restraint system complements this with pre-tensioners and load-limiters that keep occupants safely in place. Specially designed passenger airbags are shaped to protect an occupant’s head in angled or offset crashes, and active vents dynamically adjust the internal pressure of the frontal airbags to optimize protection based on the unique characteristics of the crash. Front and knee airbags and a collapsible steering column work to further reduce injury, all contributing to Model 3’s 5-star rating in frontal impact.
In pole impact crashes, in which a narrow obstruction impacts the car between the main crash rails, energy-absorbing lateral and diagonal beam structures work to mitigate the impact. This includes a high-strength aluminum bumper beam, a sway bar placed low and forward in the front of the car, cross-members at the front of the steel subframe that are connected to the main crash rails, and additional diagonal beams in the subframe that distribute energy back to the crash rails when they aren’t directly impacted. An ultra-high strength martensitic steel beam is also attached to the top of the front suspension to further absorb crash energy from severe impacts, and the rear part of the subframe is shaped like a “U” and buckles down when impacted. These structures continue to be effective even when a front motor is added for Model 3 Dual-Motor All-Wheel Drive, due to the fact that the subframe is designed to pull the nose of the motor down and out of the way.
Model 3 also has the lowest intrusion from side pole impact of any vehicle tested by NHTSA. Unlike frontal crashes, there is little room for crumple zone in a side impact, so we patented our own pillar structures and side sills to absorb as much energy as possible in a very short distance. These structures work alongside the vehicle’s rigid body and fortified battery architecture to further reduce and prevent compartment intrusion. With less intrusion into the cabin, our side airbags have more space to inflate and cushion the occupants inside.
Rollover accidents are a significant contributor to injuries and deaths on U.S. roads. Tesla’s vehicle architecture is fundamentally designed to have a very low center of gravity, which is accomplished by placing the heavy battery pack and electric motors as close to the ground as possible. In the event that a rollover does occur, our internal tests show that the Model 3 body structure can withstand roof-crush loads equivalent to more than four times its own weight and with very little structural deformation. NHTSA’s standards only require that cars withstand loads of three times their own weight.
Many companies try to build cars that perform well in crash tests, and every car company claims their vehicles are safe. But when a crash happens in real life, these test results show that if you are driving a Tesla, you have the best chance of avoiding serious injury.
 下载格隆汇APP
下载格隆汇APP
 下载诊股宝App
下载诊股宝App
 下载汇路演APP
下载汇路演APP

 社区
社区
 会员
会员